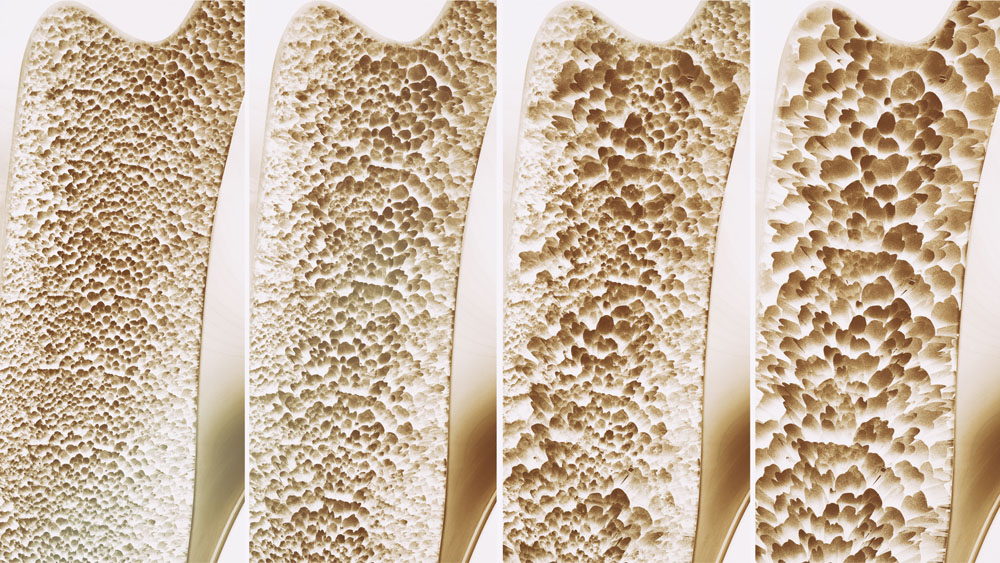
When bones lose bone salts, the appearance of the bone changes, and you can see this in the image below. It shows pieces (sections) of bone from different people, each of whom have different levels of bone salts. Use the picture to answer the questions which follow:
We can calculate the density of any material using the formula below:
Imagine that you are a pathologist in a hospital (examining dead bodies!). You have been given a sample of bone, and you need to find its density. The volume of the bone is 10 cm3, and its mass is 15g. The worked example below shows you how to calculate the value of density:
volume is 10 cm3; mass is 15g. density = mass ÷ volume density = 15 ÷ 10 density = 1.5 g/cm3
(This is a bit lower than the person in the worked example, but not dangerously low)